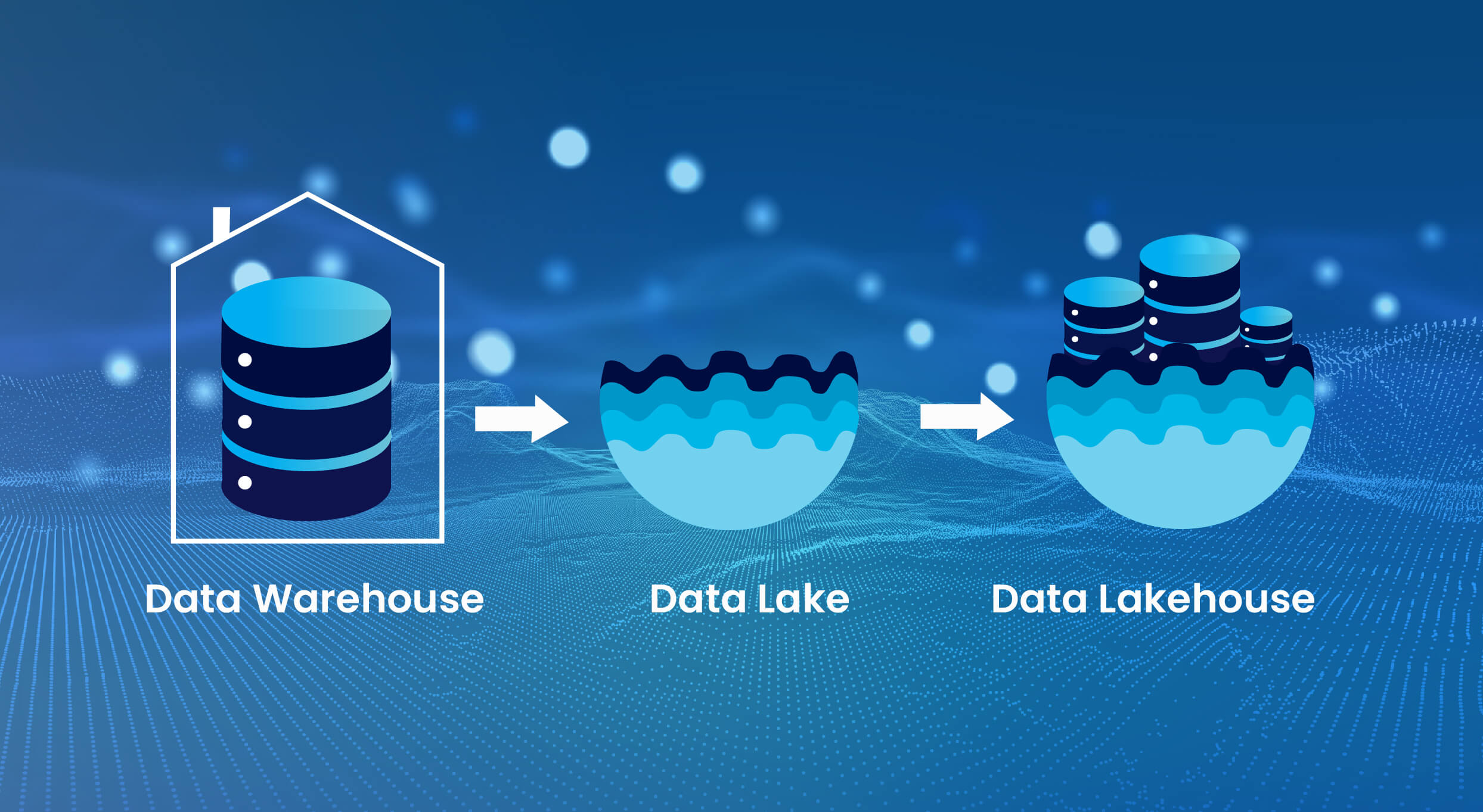
Data is not only a valuable resource but also the fundamental basis of company strategy. The management, storage, and processing of this vital resource have undergone significant changes. The conventional distinctions between data warehouses and lakes are becoming less distinct, leading to the emergence of a novel and more cohesive methodology known as the Data Lakehouse. This novel design integrates the vast storage capacities of data lakes with the organized administration and computational powers of data warehouses, providing an unmatched solution for contemporary data requirements.
In the realm of Data Lakehouse, Apache Iceberg, and Dremio are emerging as prominent contenders, each with distinct advantages. The Apache Iceberg format, which is an open table format, is increasingly becoming recognized for its resilience and adaptability in managing large data sets across many platforms. In addition, Dremio offers a complete solution that smoothly integrates with Iceberg, hence enabling enhanced data virtualization, query engine functionalities, and a resilient semantic layer.
The data warehouse services providers offer a complete platform that allows them to fully use their data by integrating the most beneficial features of data lakes and data warehouses. This blog will thoroughly explore the reasons why these technologies are not only trendy terms but also essential tools in the collection of any data-centric business.
What is a Hybrid Data Lake?
The hybrid data lake is an architectural framework for managing data that integrates the characteristics of conventional on-premises data storage with cloud-based storage components. It enables companies to efficiently store large quantities of raw data, regardless of its structure, in its original format while also facilitating flexible data processing and analysis.
The data lake’s “hybrid” nature stems from its capacity to use the benefits of both on-premises and cloud storage. On one side, on-premises storage often affords enhanced data control and expedited access under certain conditions. However, cloud storage is often characterized by its scalability and cost-effectiveness, mainly when dealing with more extensive datasets. Additionally, it offers enhanced accessibility across several locations.
A hybrid data lake strategy enables enterprises to achieve a harmonious equilibrium between these two methodologies, enabling them to make informed decisions on data storage location, taking into account several criteria like cost, performance, security, compliance, and business requirements. The ability to adapt allows an organization to enhance its data architecture to align with its business objectives and analytical requirements effectively.
Key Attentions for Shuffling to a Modern Data Warehouse
Modern data warehouses have developed to be essential for companies and provide several benefits. However, these potential often come with issues such as complications in integration, problems with cost and performance optimization, and constraints due to vendor lock-in. These prevalent obstacles usually dissuade organizations from adopting data warehouse modernization.
Nevertheless, by adopting planned methods of modernization, companies may effectively surmount these obstacles. The following guidelines may facilitate a smoother transition for a company from a conventional on-premises data warehouse to a contemporary data warehouse, enabling the organization to capitalize on the enduring advantages of modernized data infrastructure fully.
1. Conforming to the interests of business stakeholders
The cornerstone for a successful transfer lies in actively involving and cooperating with all the essential stakeholders to prioritize data and analytics activities according to business goals.
2. Effective Management of Metadata
It is crucial to implement a complete strategy for managing metadata, which encompasses several aspects such as data lineage, transformations, definitions, and more. This approach is essential for effectively tracking and documenting data throughout its entire lifespan.
3. Process of selecting appropriate tools and technologies
Each company has distinct characteristics, including a range of difficulties and capacities. Hence, it is crucial to assess and choose contemporary data warehouse techniques and technologies that most effectively align with the organization’s needs.
4. Applying Data Governance Policies
To successfully reply to altering legal requirements and industry standards, businesses must establish a complete data governance structure.
5. Management of Data across many Cloud Platforms
Multi-cloud data management refers to the use of several cloud service providers to spread data and applications. This method efficiently lessens the dangers connected with vendor lock-in, recovers the ability to withstand areas of system unavailability, and enables organizations to choose the most suitable services from a range of suppliers.
The use of Hybrid Cloud Computing presents Several Challenges
Organizations must carefully manage a variety of significant hurdles and concerns when adopting a hybrid architecture in cloud data warehousing. Ensuring a smooth interface between on-premises and cloud settings is a considerable difficulty. It entails the resolution of compatibility challenges, complexity in data synchronization, and security considerations to maintain a unified and effective data infrastructure.
Transitioning from a private or public cloud infrastructure or an in-house data center to a hybrid cloud system is a laborious and resource-demanding procedure. The existing apps and workload should possess the ability to be easily transferred and used across both on-premises infrastructure and a third-party-managed public cloud environment.
The primary objective of IT governance in the organization is the standardization of procedures. Historically, the need for governance emerged to provide supervision and guidance. The administration of a hybrid cloud, which integrates numerous systems, would be more intricate compared to the current private or public cloud systems.
Cloud Computing Expenses
The expenses associated with cloud computing may rapidly escalate, mainly when external departments contribute to the organization’s total cloud infrastructure. However, due to the primary allure of cloud computing being the potential for cost reduction, corporations find it particularly unattractive to allow a multi-cloud approach to result in excessive expenses.
In reality, API tools, as well as procedures, allow website applications, containers, and microservices to interconnect with all online firmly. Nonetheless, safeguarding APIs remains a chief problem. In a recent survey, 70.9% of respondents said poorly organized or uncertain APIs or boundaries are their significant problems. APIs could depict the app’s back-end logic and complex data, creating APIs’ primary targets for aggressors.
Conclusion: Embracing the Revolution of Data Lakehouse
Taking a look into the near future of cloud data warehousing, it is abundantly evident that hybrid architecture is going to keep playing an essential part in the industry’s development. Companies have to make preparations for significant operational shifts, as well as a reorganization of their culture, infrastructure, and procedures that involve their employees.
To facilitate this transition into the future of hybrid work, cloud-based software that assists in the management, optimization, and improvement of the workplace will emerge as an essential component. The arrival of the Data Lakehouse implies a substantial change in the manner in which many firms oversee and use their data. Cloud data warehousing provides a multitude of benefits.